A recent paper by the Salesforce AI research team describes a method for generating function-calling datasets for Large Language Models (LLMs). Function calling enables LLMs to interact with external systems, like remote APIs, databases, or in-process code. This equips LLMs with tools to perform specific actions, such as retrieving weather information, booking reservations, or fetching stock data from APIs.
If you’re unfamiliar with function calling, refer to the OpenAI docs to learn more.
This post explores practical takeaways for developers building LLM applications.
1. Fine-Tuning Performance Relies on High-Quality Data
The APIGen framework effectively generates high-quality datasets, significantly improving LLMs’ function-calling capabilities. APIGen’s rigorous filtering process, including semantic and execution checks, ensures only high-quality data is used for training, leading to better performance. Here’s a breakdown of the three stages:
- Format Checker: This initial stage filters poorly formatted or incomplete data. It ensures the output strictly follows a JSON format with required fields like “query” and “answer,” and checks for correct JSON parsing and valid arguments.
- API Execution Engine: The second stage executes the generated function calls to verify their correctness. This step ensures the calls are executable and produce valid outputs.
- Semantic Checker: The final stage involves a semantic checker, another LLM, that assesses the alignment between the function calls, execution results, and the query objectives. This stage ensures the generated data points meet the intended purpose and are relevant.
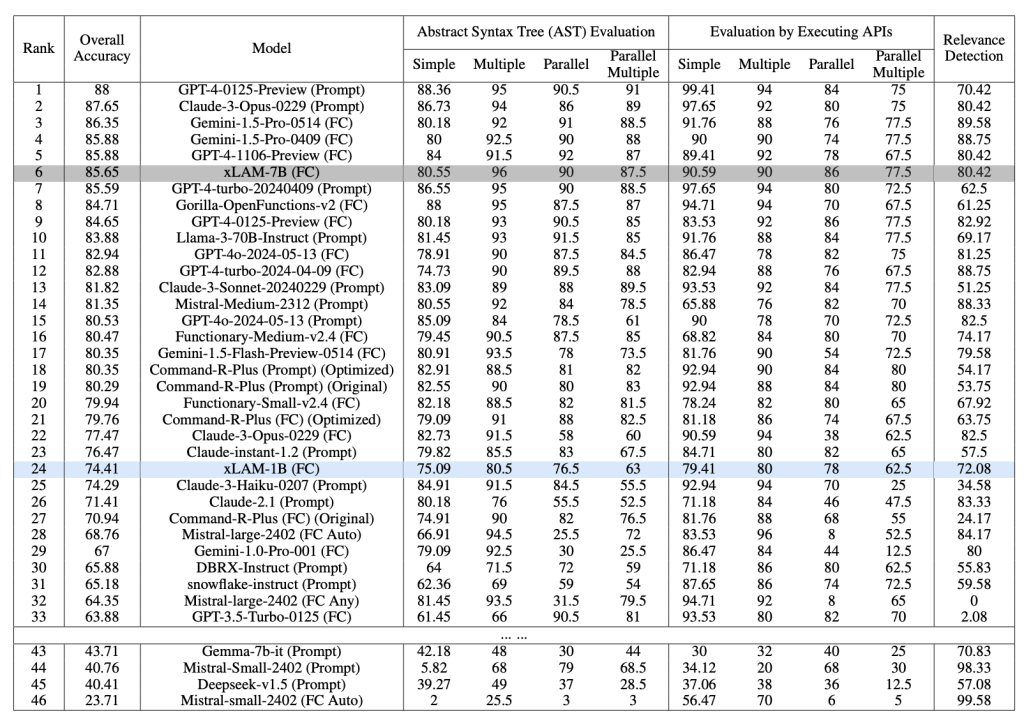
When using weaker models to generate data, a rigorous verification process becomes essential to filter out low-quality data. This ensures the model’s integrity and maintains performance. As shown in the image below, the xLAM-7B model fine-tuned on the APIGen dataset outperforms many closed-source models.
The paper also presents results of an ablation study where adding datasets filtered out by the semantic checker (stage 3) and execution checker (stage 2) back to the training set resulted in performance degradation, especially for smaller models.

2. Building Strong Automated Evaluations for Your Dataset
To ensure high data quality, you need a set of automated checks to filter out low-quality data. The paper discusses the following checks used to filter out bad data:
- Whether the function call aligns with the query’s objective and has proper arguments
- Whether the function call and arguments are chosen appropriately from available functions
- Whether the number of function calls matches the user’s intent
- Whether the execution results contain errors or indicate unsuccessful function execution
- Whether the execution results are relevant and match the query’s purpose.
Along with automated evaluation, human evaluation is also crucial. From the paper
We engage three human evaluators to manually inspect a total of 600 samples from our released dataset. The evaluators assess the quality of each sample based on factors such as the accuracy of parameter values and the appropriateness of the number of API calls.
The results of the human evaluation reveal that only 28 out of the 600 inspected samples have minor issues, such as inaccurate parameter values or more API calls than expected. This means that the majority of the data, approximately 95.3%, are of very high quality. The high quality of the dataset can be attributed to the format and execution checkers implemented in the APIGen pipeline.
Conclusion
The APIGen framework introduces an automated pipeline for generating diverse and verifiable function-calling datasets to improve the function-calling capabilities of LLMs. Evaluated using the BFCL (Berkeley Function-Calling Leaderboard), APIGen’s xLAM-7B model ranked 6th, outperforming several versions of GPT-4 and other top models, demonstrating the effectiveness of high-quality datasets in enhancing model performance. The framework emphasizes data quality, diversity, and scalability, ensuring robust evaluation and training of LLMs across various programming languages and application domains.
Discover more from Shekhar Gulati
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.